Table of Contents
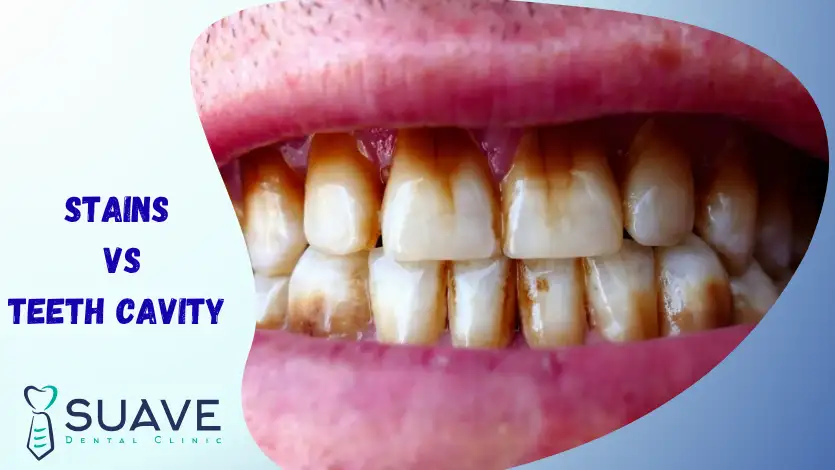
“I want to remove this stain, please, doctor.” After a careful examination, the dentist replied, “I’m sorry to say this is not just a stain; it is likely to be a cavity.” Like lots of people, I thought dark spots on teeth were simply stains that needed to be cleaned.
Surprisingly, what appears to be a harmless stain may actually be the first sign of tooth decay.
This is where the confusion between tooth cavity vs stain becomes important. Stains are mostly an aesthetic issue that can be polished away, while a tooth cavity is a real dental problem that needs immediate intervention.
What is Tooth Decay?
A damaged area of the tooth, where the enamel is broken down, resulted in a tooth hole that got deeper and bigger with time, resulting in a toothache and hot and cold sensitivity. The early stage of tooth decay is very symptomless; you can’t see anything or even feel any pain more than a non-noticeable white spot.
What is a Tooth stain?
A discoloration that appears on the outer surface of the tooth. It can be extrinsic or intrinsic.
Teeth discoloration and stains, when superfacial, are symptomless too; the only issue is the change of color and brown, black spots on the tooth surface.
The difference between a tooth cavity and stains
The initial phases of the tooth cavity are very similar to stains, which is why they are indistinguishable to us, and can only be detected by dental examination and regular check-ups
1- Origin:
- A tooth cavity is caused by dental caries, which results from bacteria and bacterial acids that break down the tooth structure, infect the dentin, and the dental pulp.
- Unlike the tooth cavity, stains are discolorations that change the color of the tooth surface, which may be superficial or deep.
2- Pain:
- Both stains and tooth cavities in the early stages are symptomless and painless; when the tooth cavity spreads inside the tooth structure, it becomes painful and causes serious symptoms.
3- Color:
- Stains on the tooth surface vary from yellowish to brown and black spots.
- At the same time, dental caries start with white spots (in areas of tooth enamel demineralization), then progress to brownish and black spots and patches, especially on tooth grooves and lateral tooth surfaces.
4- Spread:
- Superfacial Stains are almost scattered on the tooth surfaces following the calculus and tartar accumulation on teeth.
- Tooth decay initiates as white or brownish spots that get bigger and deeper with time. At the same time, the enamel demineralization damages the tooth surface, and an actual tooth cavity is formed.
5- Reversibility:
- Superfacial stains are harmless and reversible, and accumulate on the tooth surface and could be removed by professional cleaning and polishing.
Some stains are irreversible as they change the color of the enamel and dentin tooth structure as intrinsic stains.
- On the other hand, the tooth cavity is irreversible, and considered a dental issue that needs a dental intervention as fast as possible, and cannot be healed on its own.
Causes of Cavities and Stains
Both can appear similar at first glance. But the cause of a tooth cavity vs a stain is very different.
Causes of cavities:
Tooth decay happens when food debris and plaque, a sticky layer of bacteria, accumulate on the tooth surface without being brushed away. It damages the tooth surface, creating a pit or hole. Here are some risk factors of cavities.
- Poor oral hygiene: improper tooth brushing and flossing create a bacteria-rich environment that attacks teeth and gums
- Unhealthy diet: rich in sugar and starch, it fuels bacteria that cause decay.
- Dry mouth and less water intake: reduced saliva increases the risk of tooth decay. Saliva washes away food particles and neutralizes acids.
- Family history of tooth decay: a patient might inherit tooth shape from his parents (deep grooves, weak enamel), which can increase the risk of tooth decay.
Causes of stains
Tooth discoloration can happen for two main reasons. It may come from outside the tooth (External factors), or it can develop inside the tooth (internal factors). Based on this, stains are divided into extrinsic and intrinsic types.
- Extrinsic stains (outside the tooth): They affect the outer surface of the enamel, usually caused by external factors such as:
- Colored foods and drinks: coffee, tea, soda, wine, berries, and tomato sauce.
- Smoking and tobacco use.
- Poor oral hygiene allows pigments to stick to the enamel.
- Certain mouthwashes contain chlorhexidine.
- Intrinsic stains (inside the tooth): These come from within the tooth structure and are often harder to remove. Common causes include:
- Aging: With age, enamel wears and loses its translucency, revealing the yellow dentine underneath.
- Genetics: The natural color of teeth differs from one person to another.
- Excessive fluoride: excessive intake of it can cause white spots on teeth, “fluorosis.”
- Trauma: sports-related injury, falls that result in injury of pulp, and darkening of the tooth “Dead Tooth”.
- Dental treatment: when teeth are filled with amalgam filling material rich in silver, it makes teeth appear gray with an “Amalgam tattoo.”
- Medications: antibiotics (like tetracycline), antihistamines, and blood pressure drugs.
- Medical conditions: metabolic disease, calcium deficiency, liver disease, eating problems, and cancer treatments.
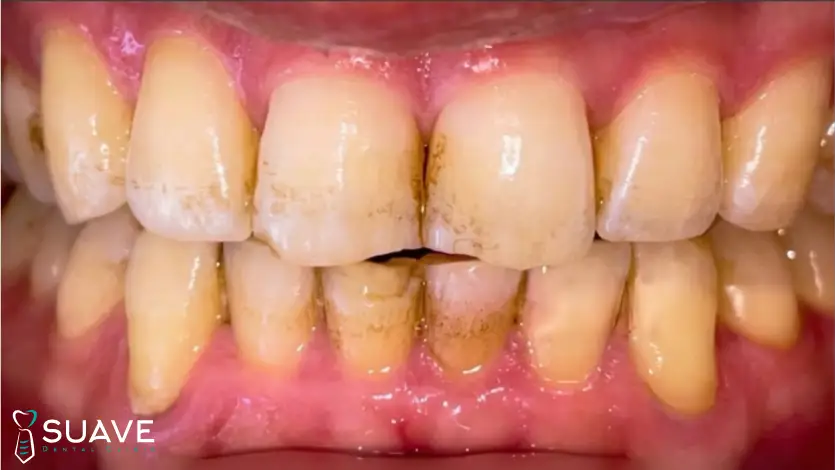
Is Tooth Discoloration Always a Cavity?
Not every tooth discoloration is always a cavity. The difference between a tooth cavity vs stain lies in the underlying cause: stains are often superficial, while decay involves damage to the tooth structure itself.
At first glance, they may look alike. That’s why only a dentist can differentiate between them after a detailed diagnosis.
How Do Stains Become Cavities?
For a stain to become a cavity, it takes more time and less concern.
It takes months to start to destroy the tooth.
- With neglected oral hygiene care for a period of time, Plaque begins to form as a sticky layer of bacteria on your teeth.
- When eating sugary or starchy foods or drinks, the favorite food for bacteria, bacteria produce acids.
- Acids attack teeth and start to destroy the enamel of the tooth, weakening it.
- Due to the stickiness of the plaque, this keeps the acid in contact with the tooth surface for a long time.
- Over time, acids break more tooth structure, creating a cavity that would get deeper, reaching dentine and pulp
That’s why we at Suave Clinic always encourage regular clinical checkups every 3 to 6 months to prevent tooth cavities and eliminate all the factors that could lead to tooth decay.
Tooth Stains vs Tooth Cavity Treatments
When it comes to tooth cavity vs stain, treatment is completely different because the cause itself is different.
How to stop a cavity from growing?
To stop a cavity from growing, you must go to the dentist as soon as possible. There are many interventions. Depending on the stage of decay, treatment options may include:
- Fluoride application: In the very early stage of cavity formation, clinical fluoride application could be used to repair damaged enamel, which is known as remineralization.
- Tooth filling: dental filling is the simplest treatment; cleaning from bacteria and debris and filling the cavity with a tooth-colored material to restore shape and function.
- Dental Crown: When a tooth is badly decayed and becomes weak, we use a crown cap to stop further decay and strengthen the tooth.
- Root canal treatment: This is the last option before you lose your tooth. As decay reaches the pulp and damages it. So, infected pulp is removed, and the tooth is saved with a biocompatible filling material.
Can tooth stains be removed?
Unlike cavities, stains and teeth pigmentations are a cosmetic issue and can often be managed with some commitment to a particular oral hygiene routine. Treatment depends on the cause and includes:
- Good oral hygiene: The most important thing to prevent new stains.
- Scaling and polishing: professional dental cleaning removes plaque and debris from the tooth surface.
- Teeth whitening: through various whitening products (rich in hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide), office bleaching, home bleaching, or whitening toothpaste.
- Dental bonding or veneers: if stains are resistant to whitening, cosmetic restorations can improve appearance.
The Cost of Tooth Stains vs Cavity Treatment Options
When comparing tooth cavity vs stain, the cost of treatment differs widely because the cause of the problem is not the same.
- Tooth discoloration is a superficial stain, so treatment is often simpler and less expensive; it just cleans them away.
- Tooth decay takes a long time to happen and causes deeper damage, so it needs a complicated and costly treatment to fix what happens over the years.
Get A Free Dental Consultation
Get A Personalized Treatment Plan and Quotation
Daily Routine to Avoid Stains and Cavities
When it comes to tooth cavity versus stain, prevention is always better than treatment. A proper daily routine can help you protect your teeth and avoid stains and cavities
- Maintain good oral hygiene
- Brushing at least twice a day, each time for 5 minutes.
- Flossing after meals to remove any food remaining
- Use fluoridated toothpaste regularly.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Avoid colored foods and sauces.
- Avoid excessive dark beverages like coffee, alcohol, and so..
- Avoid smoking or tobacco products.
- Use Pit and fissure sealant to protect deep grooves from food impaction as a dental preventive treatment.
- Use fluoridated, antibacterial mouthwash to strengthen your teeth and reduce plaque.
- Regular visits to the dental office for checkups and early detection of any tooth decay
By following these steps, you can keep your teeth healthy and free from both stains and cavities.
Knowing the difference between a tooth cavity and a stain is essential for protecting your oral health. By following a proper oral hygiene routine, you can prevent tooth decay and stains. If you notice a dark spot on your tooth, the safest step is to see a dentist.
Tooth Cavity vs Stain FAQs
How to get rid of stains in the grooves of teeth?
See a dentist to determine if these stains are merely discoloration or a sign of tooth decay. Superficial stains may be removed with an electric toothbrush, while deeper stains need professional cleaning at the dental office.
Are brown spots on teeth always cavities?
No, not always. But if these spots are visible and accompanied by pain or sensitivity, they are more likely to be a sign of tooth decay.
How long can a cavity go untreated?
According to oral health conditions, the patient’s immune system, diet, and daily routine, tooth decay should never be left untreated. It could range from a couple of days to months.
What does an early-stage cavity look like?
The early stage of a cavity is a chalky white spot due to enamel demineralization.
Over time, acids from bacteria turn it into a darker brown or black lesion.
What toothpaste is best for cavities?
Toothpaste by itself can’t treat decay. But for preventing tooth decay, a fluoridated toothpaste is essential to strengthen enamel and protect the remaining healthy structure, so any fluoride-containing toothpaste will do the job.
Can a cavity heal on its own?
This could happen in only one situation, when at the early stage of decay, fluoride application is used to repair the enamel. But once decay spread deeper beyond the enamel, it could not heal on its own.
Can flossing prevent cavities?
Flossing can reduce the likelihood of cavities, but not 100%. However, it should be combined with brushing, fluoride use, and checkups every 3-6 months.
References
Medically Reviewe